LiDAR technology has revolutionized the field of robotics, providing robots with the ability to accurately perceive and navigate their environment in real-time. LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, uses a laser beam to measure distances to objects and surfaces, creating a 3D map of the robot’s surroundings. This technology has been crucial in the development of autonomous robots, from self-driving cars to drones, and has a wide range of applications in various industries.
How does LiDAR work?
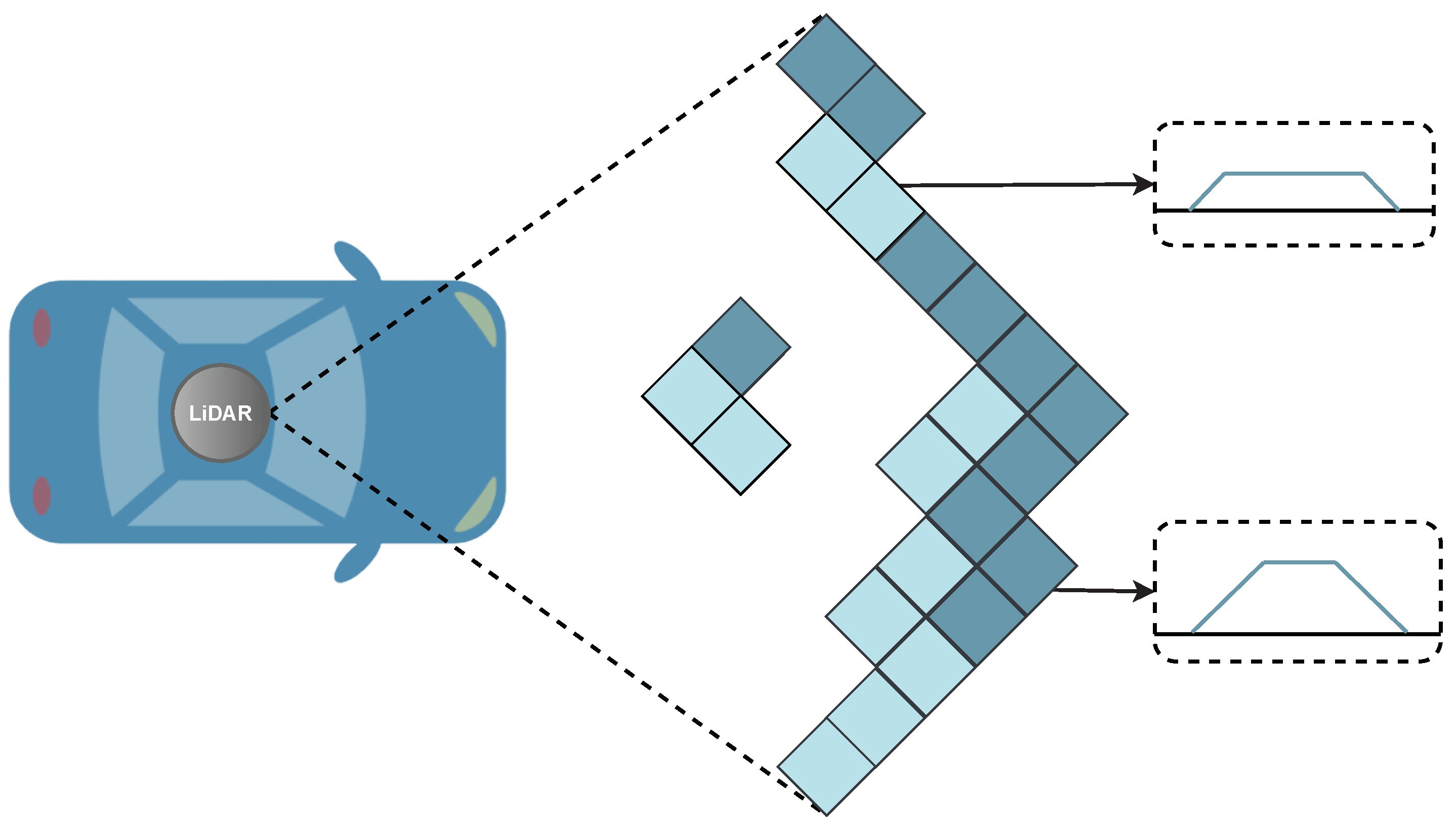
A LiDAR system emits short bursts of laser light towards a target area. These laser pulses bounce off objects in the environment, and the sensor then measures the time it takes for the pulses to return. By knowing the speed of light, the system calculates the distance to each object with remarkable precision. By scanning the laser pulses across the field of view and combining the distance measurements, LiDAR generates a 3D representation of the terrain and objects in its range.
Where is LiDAR used?
One of the most significant applications of LiDAR technology is in autonomous vehicles. LiDAR sensors mounted on self-driving cars can create a real-time 3D map of the car’s surroundings, allowing the car to navigate and make decisions based on its environment. This technology is also used in drones, both for navigation and for creating detailed 3D maps of the terrain. By providing robots with the ability to perceive and understand their environment, LiDAR technology has made it possible for autonomous vehicles to safely and efficiently navigate in complex and dynamic environments.
4. ADIBOT-A and ADIBOT-S are now the A1 and S1
As part of our brand refresh, we’ve made a few adjustments regarding the naming of our current solutions. The ADIBOT-A is now the A1, and the ADIBOT-S is now the S1. These updates reflect our commitment to clarity and simplicity while maintaining the same exceptional performance you’ve come to expect.
Another application of LiDAR technology is in the field of logistics and supply chain management. LiDAR-equipped robots can be used in warehouses and distribution centers to perform tasks such as inventory management, package sorting, and order fulfillment. These robots use LiDAR to create a 3D map of the warehouse and to locate and pick up specific items. By automating these tasks, LiDAR technology has the potential to improve efficiency and reduce labor costs in the logistics industry.
How LiDAR Enables Effective UV-C Disinfection
In the context of autonomous UV-C disinfection, LiDAR plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency and safety of the disinfection process. LiDAR sensors are integrated into UV-C disinfection robots or devices, like the ADIBOT A1, to accurately map and navigate the environment. These sensors create detailed 3D maps of the surroundings, identifying obstacles and potential hazards. By analyzing these maps in real-time, the UV-C disinfection system can autonomously plan and adjust its path, ensuring thorough coverage and avoiding collisions with objects or individuals in the area.
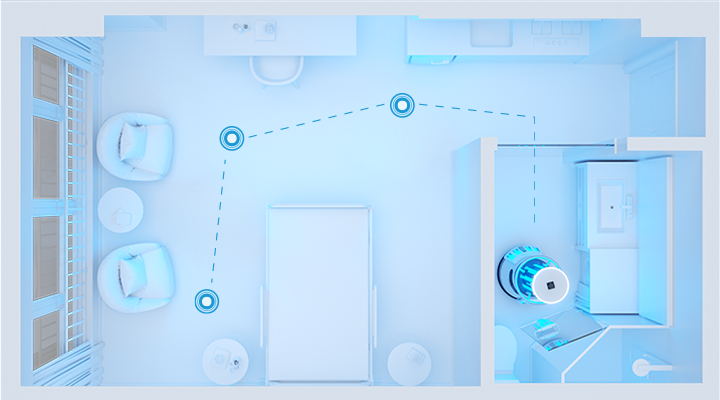
LiDAR’s ability to provide precise spatial awareness complements UV-C disinfection by allowing robots to navigate close to contaminated surfaces, maximizing effectiveness in inactivating pathogens. Together, they create a powerful solution for automated disinfection in various settings, such as hospitals, transportation hubs, and public spaces, reducing the risk of human error and improving overall disinfection outcomes.
As the technology continues to improve and costs continue to decline, we can expect to see even more applications for LiDAR in robotics in the future.